What is a worker ?
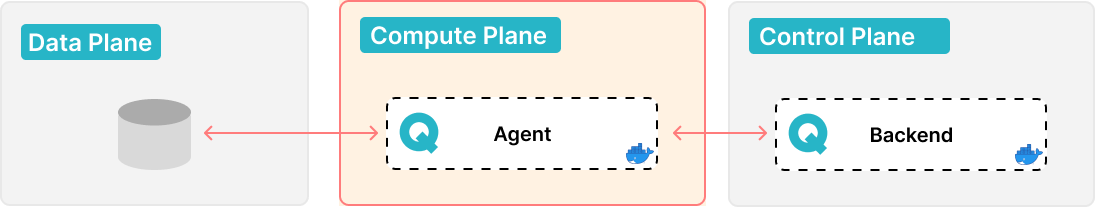
QALITA workers are workers for the platform and sources. They connect them together and compute analysis, then send them to the platform.
Deploy a Worker
Workers must be installed the closest possible to the source as they will interact with them. take into account network configuration (proxy/firewall) and bandwidth for databases, or IO disk usage for files and no-SQL sources.
Hardware Requirements
Worker characteristics depend heavily on the typology and volume of sources for which they perform analysis.
| Usage | Memory | CPU | GPU |
|---|---|---|---|
| Minimal | 50 MiB | 0.2 | NVIDIA RTX 5060 Ti (for Studio) |
| Depends on source volume and analysis frequency | . | . |
NVIDIA GPU are recommended when using worker in UI mode and using Studio
Modalities
| Method | Description | Documentation |
|---|---|---|
| Desktop | Use your Terminal to deploy a local worker on your workstation. | CLI > Quick Start |
| Docker | Deploy a worker using Docker. | CLI > Docker |
| Kubernetes | Deploy a worker with the qalita helm chart and enable the worker flag. | See the documentation for available configuration options. |
You will then see your worker in the platform's worker page.
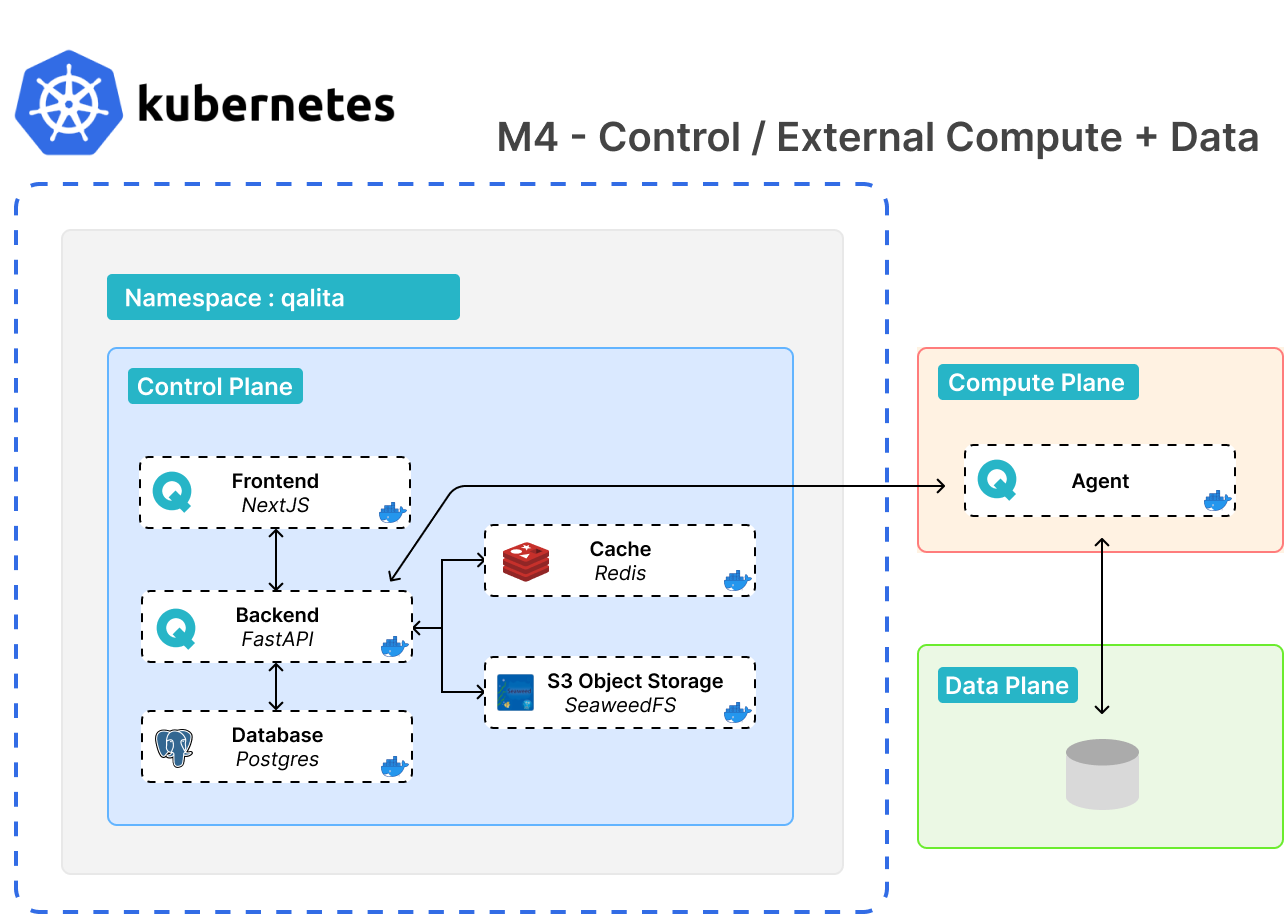
(Advanced) Kubernetes Architecture details
Same namespace
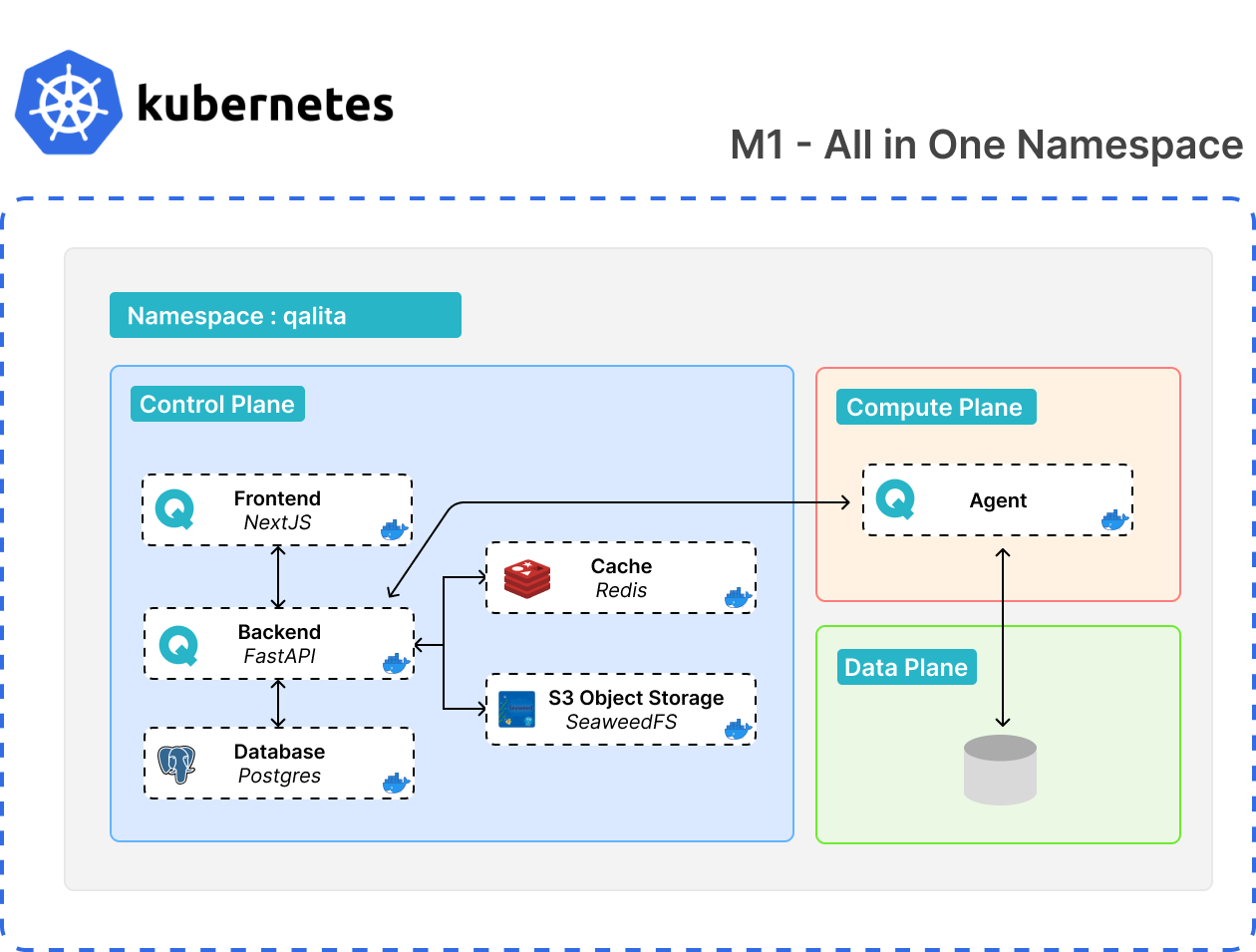
- Deployment with worker in the same namespace
worker.enabled=true - Deployment of data sources in the same namespace
Different namespace
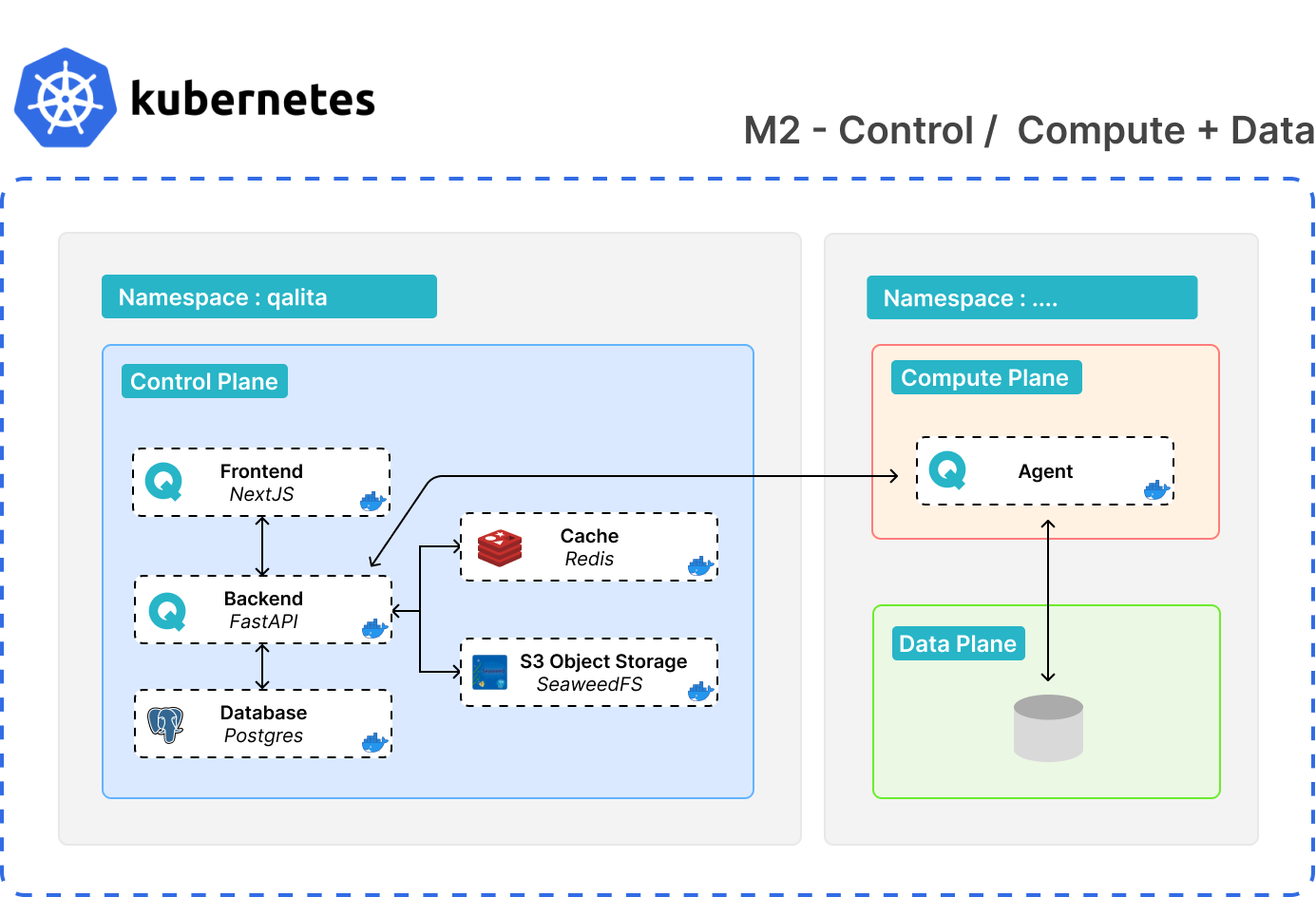
- Deployment of a worker in another namespace
- Deployment of data sources in the same namespace
Different namespace + remote source
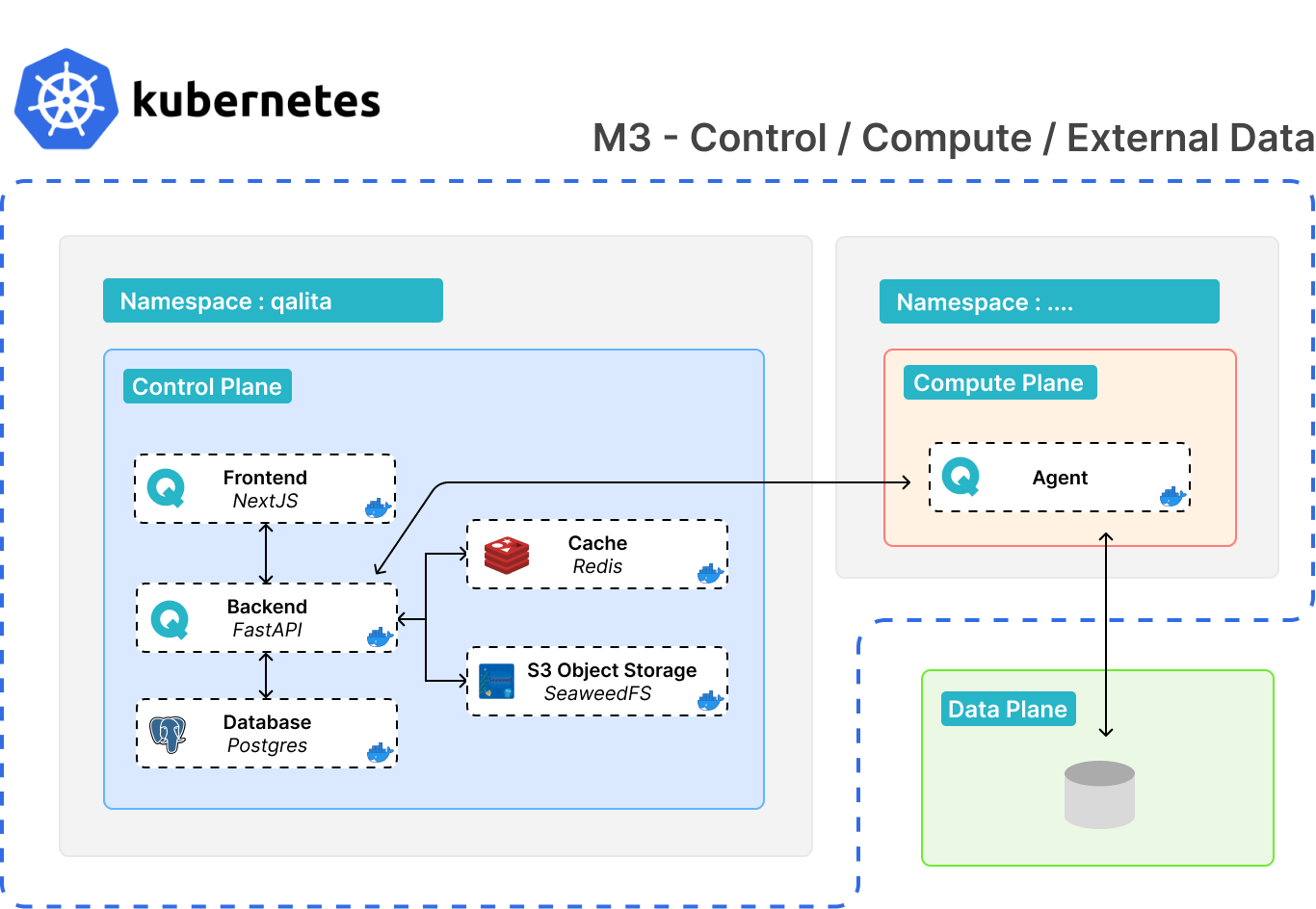
- Deployment of a worker in another namespace
- To connect to a source in any other environment (VM, localhost, etc.)
Fully Remote
- Deployment of a worker in any other environment (VM, localhost, etc.)
- To connect to a source located in any other environment (VM, localhost, etc.)
Worker Operating Modes
The worker has 2 operating modes:
Job
Job mode can be useful when developing your own packs. To run a pack in job mode, you will need:
- A source registered on the platform
- A pack registered on the platform
You will need to get their ID with:
qalita source list
and
qalita pack list
Finally, you can run a job locally with your worker using:
qalita worker -m job run -s <source_id> -p <pack_id>
This will run your pack with your source using your local worker.
This Helps you debug your packs when developping them allowing fast itteration.
Worker
Worker mode allows you to run a worker as a worker for the platform. It allows you to run tasks and routines in the background.
This worker will remain online waiting for tasks to execute.
Worker mode workers will only run tasks on sources that they have in their configuration ~/.qalita/sources-conf.yaml. If the source is not present with an id in the worker's configuration, it will not be able to run tasks on that source.
Make sure your worker in worker mode has the configuration of the sources on which you want to run tasks. And that there is indeed a source id. meaning the source has been referenced to the platform.
Routines (scheduled tasks)
Create Routines
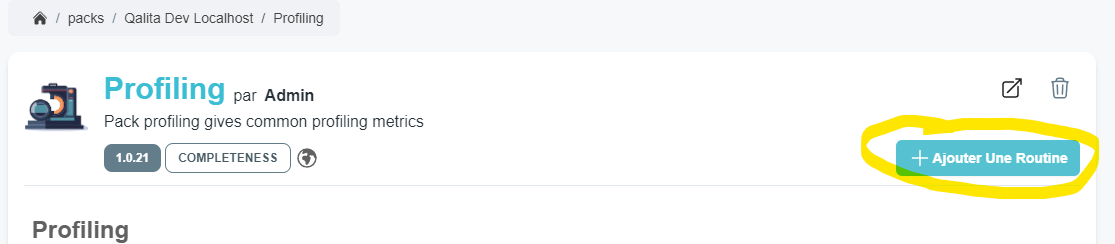
Routines are scheduled tasks that run automatically at a given schedule by any compatible workers. You can create routines from a pack's detail page.
| From a Pack Page | From a Source Page |
|---|---|
|
|
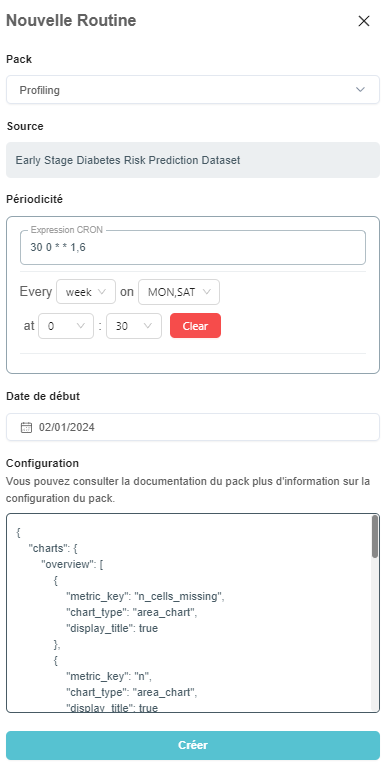
The routine creation panel allows you to select the pack to use, the frequency of routine execution, the start date of the routine. Once the pack is selected, the default configuration is loaded. You can then override the default pack configuration specifically for this routine. You can expand the pack's documentation drawer to understand better what config is most suited for your needs.
Quick Run
The Quick Run Feature allows you to create a routine in just one click.
When clicking on it on a source page, it will select and create a routine using the first available Pack compatible with your source, and specific for that data quality dimension.
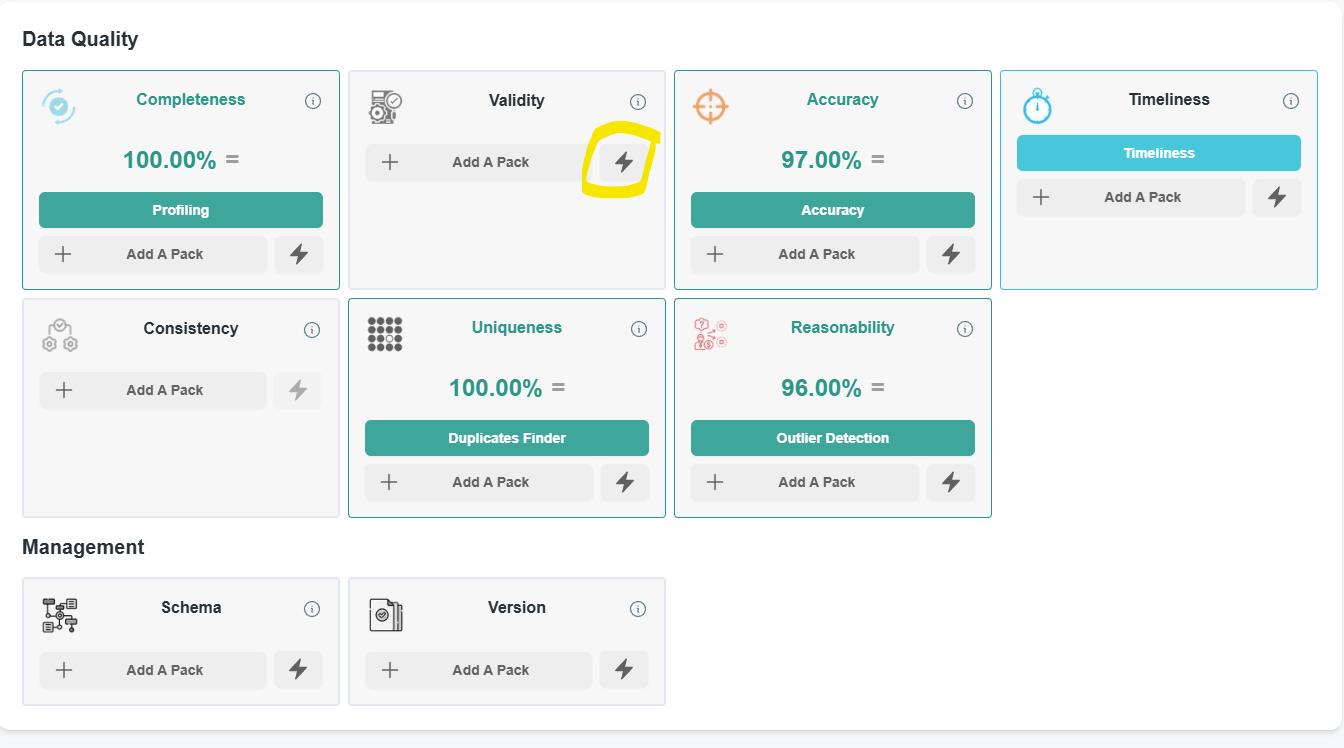
You will still be able to edit or remove the routine in the worker page.
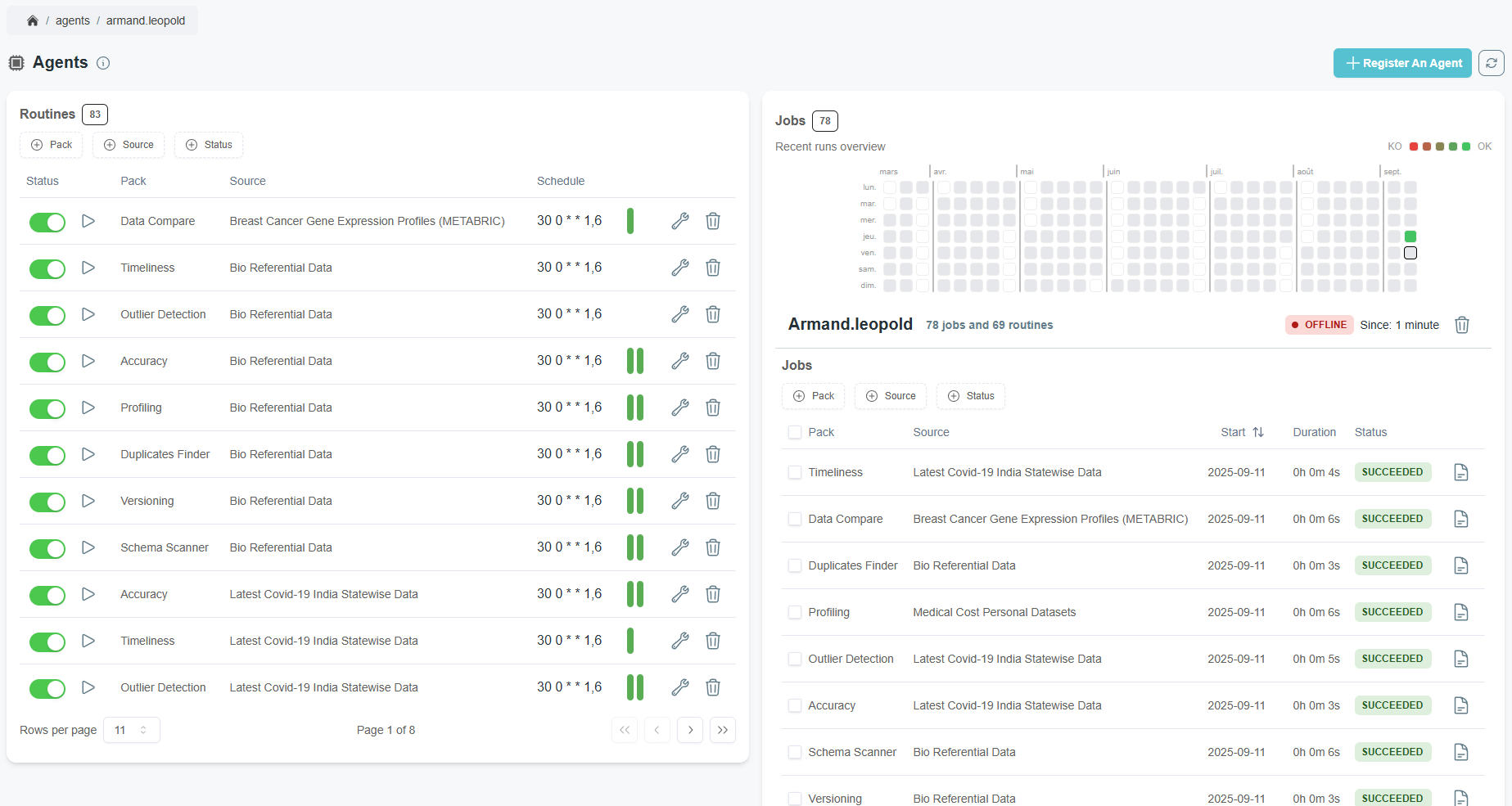
Track Routine Executions
You can track routine executions on the platform's worker page:
- View the status of tasks
- Check the logs of a task
- Enable or disable a routine
- Trigger immediately a routine will generate a task to be executed immediately.
- Modify the configuration of a routine
- Delete a routine